Jenny Harris, of Baltimore, protests in support of birthright citizenship and the immigrant community, Thursday, May 15, 2025, outside of the Supreme Court in Washington. (AP Photo/Jacquelyn Martin)
WASHINGTON (AP) — A divided Supreme Court on Friday ruled that individual judges lack the authority to grant nationwide injunctions, but the decision left unclear the fate of President Donald Trump’s restrictions on birthright citizenship.
The outcome was a victory for the Republican president, who has complained about individual judges throwing up obstacles to his agenda.
But a conservative majority left open the possibility that the birthright citizenship changes could remain blocked nationwide. Trump’s order would deny citizenship to U.S.-born children of people who are in the country illegally.
The cases now return to lower courts, where judges will have to decide how to tailor their orders to comply with the high court ruling, Justice Amy Coney Barrett wrote in the majority opinion. Enforcement of the policy can’t take place for another 30 days, Barrett wrote.
The justices agreed with the Trump administration, as well as President Joe Biden’s Democratic administration before it, that judges are overreaching by issuing orders that apply to everyone instead of just the parties before the court.
The president, making a rare appearance to hold a news conference in the White House briefing room, said that the decision was “amazing” and a “monumental victory for the Constitution,” the separation of powers and the rule of law.
In dissent, Justice Sonia Sotomayor wrote, “The court’s decision is nothing less than an open invitation for the government to bypass the Constitution.” This is so, Sotomayor said, because the administration may be able to enforce a policy even when it has been challenged and found to be unconstitutional by a lower court.
Rights groups that sued over the policy filed new court documents following the high court ruling, taking up a suggestion from Justice Brett Kavanaugh that judges still may be able to reach anyone potentially affected by the birthright citizenship order by declaring them part of “putative nationwide class.” Kavanaugh was part of the court majority on Friday but wrote a separate concurring opinion.
States that also challenged the policy in court said they would try to show that the only way to effectively protect their interests was through a nationwide hold.
“We have every expectation we absolutely will be successful in keeping the 14th Amendment as the law of the land and of course birthright citizenship as well,” said Attorney General Andrea Campbell of Massachusetts.
Birthright citizenship automatically makes anyone born in the United States an American citizen, including children born to mothers in the country illegally. The right was enshrined soon after the Civil War in the Constitution’s 14th Amendment.
In a notable Supreme Court decision from 1898, United States v. Wong Kim Ark, the court held that the only children who did not automatically receive U.S. citizenship upon being born on U.S. soil were the children of diplomats, who have allegiance to another government; enemies present in the U.S. during hostile occupation; those born on foreign ships; and those born to members of sovereign Native American tribes.
The U.S. is among about 30 countries where birthright citizenship — the principle of jus soli or “right of the soil” — is applied. Most are in the Americas, and Canada and Mexico are among them.
Trump and his supporters have argued that there should be tougher standards for becoming an American citizen, which he called “a priceless and profound gift” in the executive order he signed on his first day in office.
The Trump administration has asserted that children of noncitizens are not “subject to the jurisdiction” of the United States, a phrase used in the amendment, and therefore are not entitled to citizenship.
But states, immigrants and rights groups that have sued to block the executive order have accused the administration of trying to unsettle the broader understanding of birthright citizenship that has been accepted since the amendment’s adoption.
Judges have uniformly ruled against the administration.
The Justice Department had argued that individual judges lack the power to give nationwide effect to their rulings.
The Trump administration instead wanted the justices to allow Trump’s plan to go into effect for everyone except the handful of people and groups that sued. Failing that, the administration argued that the plan could remain blocked for now in the 22 states that sued. New Hampshire is covered by a separate order that is not at issue in this case.
The justice also agreed that the administration may make public announcements about how it plans to carry out the policy if it eventually is allowed to take effect.

Fake clinics, real harm: Crisis pregnancy centers in Nevada are duping pregnant women
“If there was a fake cancer clinic giving out false treatments, we’d all be outraged.” Imagine you need to seek treatment for diabetes, cancer, or...

Nevada just made teen abortion way harder—even in the worst situations
Imagine you’re a teen in foster care, and you’re pregnant. The father is your abusive foster parent. Nevada’s newly enforced parental notification...
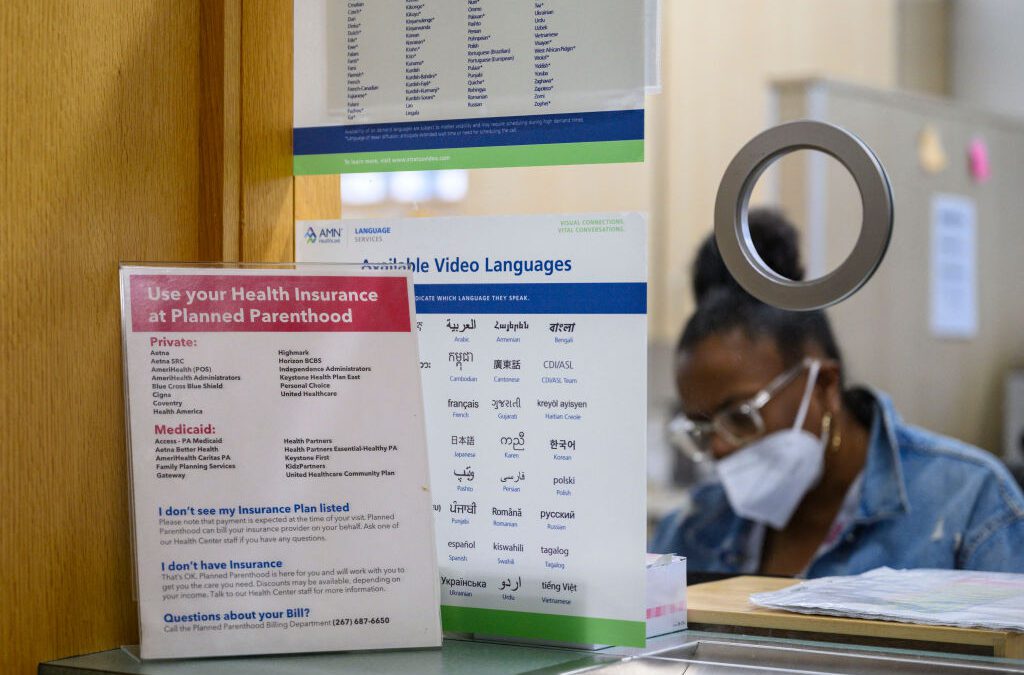
It’s Nevadan women and families taking the hit as Planned Parenthood scales down services due to federal Medicaid cuts
While none of the Planned Parenthood clinics in Nevada will be closed, certain services accessed by thousands, including prenatal care and family...

Gov. Lombardo vetoes bill to protect IVF in Nevada
A bill that would have protected in vitro fertilization, as well as expanded access to fertility treatments, was recently vetoed by Gov. Joe...

Did Gov. Joe Lombardo just sign a dangerous veto for reproductive care? This Nevada doctor says yes
Dr. Margaux Lazarin said she isn’t worried about patients having info about doctors—she’s concerned about who else might see the prescription...

Trump administration revokes guidance requiring hospitals to provide emergency abortions
WASHINGTON (AP) — The Trump administration announced on Tuesday that it would revoke guidance to the nation's hospitals that directed them to...




